GStreamer란?
스트리밍 미디어 응용 프로그램을 만들기 위한 프레임 워크로 모든 유형의 스트리밍 멀티미디어 응용 프로그램을 작성할 수 있습니다. 구성요소를 임의의 파이프라인에 혼합하여 응용 프로그램을 작성할 수 있는 장점이 있습니다.
GStreamer 구성요소
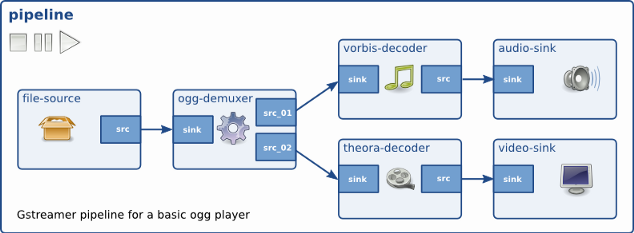
1. Pipeline
GStreamer 파이프라인은 멀티미디어 데이터를 처리하는 element들로 구성되어 있습니다.
데이터가 입력되는 src 요소와 출력되는 sink 요소, encoding, decoding filtering 등의 특정 작업을 수행하는 요소들이 존재합니다.

2. Elements
Elements는 파이프라인을 구성하는 추상화된 Block형태를 정의합니다. 서로 연결된 elements를 만들고 이를 통해 데이터가 흐르도록 합니다. source element로 시작하여 filter , demuxer, decoder 등의 element가 중간에 역할을 하며 sink element로 끝나게 됩니다.
3. Pads
각 elements를 연결하는 입력(src), 출력(simk)을 pad라고 정의합니다. 각 pad는 caps negotitation라고 불리는 과정을 통해 element 끼리의 연결을 만듭니다. 데이터는 한 방향으로만 흐르며, 데이터는 src pads 통해 나가고 sink pads 통해 받습니다.
4. Bin
Elements의 집합 컨테이너 단위입니다. 애플리케이션의 많은 복잡성을 추상화할 수 있게 합니다. bin 자체의 상태를 변경함으로써 모든 elements의 상태를 변경할 수 있습니다. pipeline 또한 bin의 큰 개념이라고 볼 수 있습니다.
GStreamer 사용법
gst-launch는 파이프라인을 CLI로 테스트해 볼 수 있는 명령어입니다. 각 elements들을 느낌표로 구분하여 사용합니다.
gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc ! autovideosink위의 커맨드를 실행하면 아래와 같은 애니메이션 비디오 패턴 창이 나타납니다,

이번에는 File 동영상을 play하는 파이프라인입니다.
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc name=src location=/home/aaa/video.mp4 ! decodebin ! autovideosink
위의 CLI 대신 c++ 구현은 아래와 같습니다.
// Streaming.h
#ifndef __STREAMING_H_
#define __STREAMING_H_
#include <gst/gst.h>
#include <gst/app/gstappsink.h>
class Streaming
{
public:
Streaming();
~Streaming();
bool start(const std::string& filePath);
void stop();
private:
bool createGstPipeline();
void destroyGstPipeline();
private:
GstElement* mPipeline;
GstBus* mBus;
std::string mFilePath;
};
#endif /* __STREAMING_H_ */// Streaming.cpp
#include "Streaming.h"
#include <sstream>
#include <gst/app/gstappsrc.h>
#include <errno.h>
Streaming::Streaming()
: mPipeline(NULL),
mBus(NULL)
{
gst_init(NULL, NULL);
}
Streaming::~Streaming()
{
destroyGstPipeline();
}
bool Streaming::start(const std::string& filePath)
{
mFilePath = filePath;
createGstPipeline();
const GstStateChangeReturn result = gst_element_set_state(mPipeline, GST_STATE_PLAYING);
if (result == GST_STATE_CHANGE_FAILURE)
{
printf("GStreamer: unable to start playback\n");
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Streaming::stop()
{
gst_element_set_state(mPipeline, GST_STATE_NULL);
destroyGstPipeline();
}
bool Streaming::createGstPipeline()
{
GError* err = NULL;
std::ostringstream stream;
stream << "filesrc name=src location=" << mFilePath;
stream << " ! decodebin ! autovideosink name=sink";
mPipeline = gst_parse_launch(stream.str().c_str(), &err);
if (err != NULL)
{
printf("createGstPipeline() failed to create pipeline (%s)\n", err->message);
return false;
}
GstPipeline* pipeline = GST_PIPELINE(mPipeline);
mBus = gst_pipeline_get_bus(pipeline);
GstElement* src = gst_bin_get_by_name(GST_BIN(pipeline), "src");
GstElement* sink = gst_bin_get_by_name(GST_BIN(pipeline), "sink");
g_object_set(src, "do-timestamp", FALSE, NULL);
g_object_set(sink, "sync", FALSE, NULL);
return true;
}
void Streaming::destroyGstPipeline()
{
if (mPipeline)
{
gst_object_unref(GST_OBJECT(mBus));
mBus = NULL;
gst_element_set_state(mPipeline, GST_STATE_NULL);
gst_object_unref(GST_OBJECT(mPipeline));
mPipeline = NULL;
}
}// Main.cpp
#include "Streaming.h"
int main(UNUSED_PARAM int argc, UNUSED_PARAM char** argv)
{
Streaming streaming;
streaming.start("/home/aaaa/video.mp4");
return 0;
}'Embedded SW 기초 > Streaming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프레임 (GOP) & 영상 품질 요소 ( Bit rate / Frame rate) (0) | 2024.05.29 |
|---|---|
| Stream 구조와 원리 (0) | 2024.05.23 |